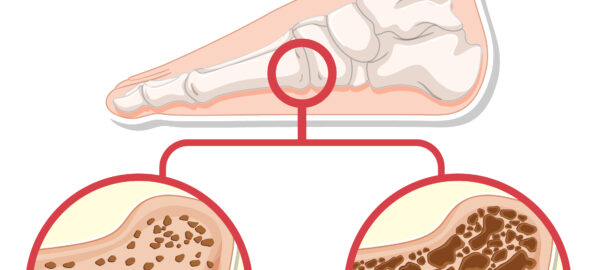
Treating foot osteoporosis involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, medications, and sometimes surgical interventions. Here are some common treatments and strategies:
- Calcium and Vitamin D Supplementation: Adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D is essential for maintaining bone health. Many individuals with osteoporosis require supplements to ensure they are getting enough of these nutrients. Your healthcare provider can advise you on the appropriate dosage.
- Medications: There are several medications available to treat osteoporosis by either slowing down bone loss or increasing bone density. These may include:
- Bisphosphonates: These drugs help to slow down bone loss and reduce the risk of fractures.
- Hormone therapy: Estrogen replacement therapy or selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) may be prescribed for postmenopausal women to help prevent bone loss.
- Denosumab: This medication is a monoclonal antibody that helps to decrease bone breakdown and increase bone density.
- Teriparatide: This medication is a synthetic form of parathyroid hormone that stimulates new bone formation.
- Lifestyle Changes: Engaging in weight-bearing exercises, such as walking, dancing, or strength training, can help improve bone density and overall bone health. It’s also important to avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption, as these habits can contribute to bone loss.
- Fall Prevention: Since fractures in the feet can occur due to falls, taking steps to prevent falls is crucial. This may involve removing tripping hazards from your home, wearing supportive footwear, using assistive devices like canes or walkers if necessary, and improving balance and strength through exercise.
- Foot Care: Proper foot care is important for individuals with foot osteoporosis to prevent complications such as foot deformities or ulcers. This may include wearing supportive shoes, using orthotic inserts, and maintaining good hygiene to prevent infections.
- Surgical Interventions: In some cases, especially if a fracture has already occurred and is severe, surgical intervention may be necessary to stabilize the bones in the foot and promote healing.
It’s essential to work closely with a podiatrist to develop a treatment plan that addresses your individual needs and monitors your progress over time. They can also provide guidance on preventive measures and lifestyle adjustments to help manage foot osteoporosis effectively.